By: Prof. Dr. Walid ‘Abd al-Hay.[1]
(Exclusively for al-Zaytouna Centre).
Introduction
Despite the confusion in many writings between “geopolitics” and “geostrategy,” especially in Arabic writings, and despite their overlapping with political geography,[2] we will focus on the geostrategic dimension of the Arab region from a specific angle, which is international projects in the Middle East. We will limit research to Asian projects that may involve competition which might develop from competition to tension, dispute and conflict. After the beginning of the waning of Western influence and its “relatively” contemporary projects, such as the New Middle East, the Greater Middle East and the Arab NATO, two important Asian projects emerged: China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) announced in 2013, and the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) announced in 2023.
| Click here to download: >>Academic Paper: The Arab Levant: From Western to Asian Competition … Prof. Dr. Walid ‘Abd al-Hay |
First: The Chinese Project
Map of the Chinese Belt and Road Initiative
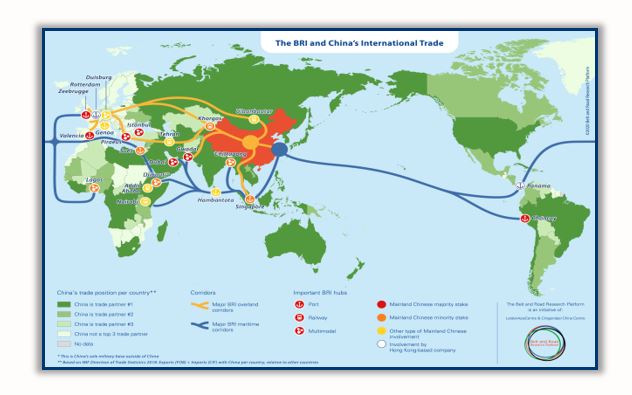
Throughout 1949–1967, the Arab-Chinese relationship was captive to an ideological perspective (except for the period 1949–1955, when the picture of the Arab-Zionist conflict was unclear among the Chinese leadership). However, the transformation in this relation went through a transitional phase (1976–1978), then a gradual, quiet, pragmatic perspective prevailed leading to Saudi recognition of China in 1990, and Chinese recognition of Israel in 1992, thus opening the way for the growth of the Chinese-Middle Eastern relationship which was crowned by the BRI announced in 2013.[3]
An academic study compares the motives and obstacles of Chinese-Middle Eastern relations, especially Arab relations, as follows:[4]
1. Chinese motives: Or the factors for growth in Arab-Chinese relations:
a. The predominance of pragmatism in Chinese political discourse and behavior since 1978.
b. The collapse of the Soviet Union has strengthened Chinese pragmatism since 1990.
c. China’s increasing need for Arab oil, especially in conservative Arab countries, due to China’s achievement of record economic growth rates.
d. The absence of pretexts for “democracy, human rights and bias toward certain religious sects over others, or ethnic tendencies (Kurdish, Berber or other)” in Chinese foreign policy.
e. China does not link its aid or its overall relations with the Arab world to strategic political conditions, military presence or particular way of voting in international organizations.
f. The increasing Arab tendency among Arab political elites, especially the new ones, to free themselves from the weight of some Western conditions for the relationship with them.
g. The attractive force of the Chinese economic and technological development model has constituted an important factor in Arab awareness to the relationship with China.
h. The rationality of Chinese decisions concerning the relationship with Arab countries, due to the increase in Chinese specialists in Arab affairs, the expansion of Arabic language teaching in Chinese universities, the spread of Confucius Institutes for teaching Chinese, and the increase in the number of Arab students in Chinese universities.
i. The expansion of the base for Arab-Israeli normalization has lifted Chinese embarrassment regarding deepening its relations with Israel since 1992.
j. The size of the Arab market on the one hand, and the large purchasing power of an important sector of this market’s consumers on the other hand, constitute an attractive force so that Chinese commodity orientation would be towards the region.
2. The obstacles to the development of Arab-Chinese relations: These include the following:
a. The extent to which Chinese economic pragmatism and even mercantilism can curb the political, ideological and military influences of the Chinese Communist Party and some Chinese political elites in the long term. In China, there is a movement led by one of their most prominent thinkers, Wang Jisi, who calls on China to fill the void resulting from the US retreat in the Arab region by expanding its diplomatic and economic presence there. Another Chinese thinker, Qu Xing, head of the China Institute of International Studies, sees the necessity of pushing the US to immerse itself in the problems of the Middle East to deviate from restricting Chinese interests in the Pacific Basin.[5] This might be the background behind the tendency of Chinese project experts to expect that the next ten years will witness a shift in the strategy of the BRI, supplementing it with security and political doses.[6]
b. A significant percentage of Chinese projects and development aid pledges have not been fulfilled or have not been completed according to the proposed plan, which reduces the credibility of the hoped-for Chinese projects. According to Chinese official reports, the level of direct foreign investments has declined, and there are projects that have been stopped, not to mention the Chinese focus on some sectors that are less important to the countries participating in the BRI, in addition to the burden of Chinese debt interest on the Belt and Road countries as Chinese interest ranges between 4.5 and 6%.[7]
c. The corruption and instability in the region may greatly confuse Chinese plans to develop its relations with Arab sides. Given that the rate of political instability in the Arab region is the highest among other political regions, this makes the Chinese project vulnerable to radical transformations in the coming years, which pressures Chinese diplomacy to work on enhancing political stability variables. Taking into account that 23% of the BRI projects in 2022 were in the Middle East, an increase of about 6.5% compared to 2021, we realize why China will work to expand its circle of political mediations to ensure a safe environment for its initiative. This explains the mediation between Saudi Arabia (KSA) and Iran and the possibilities of increasing Chinese diplomatic role in settling the Palestine issue.
d. The US determination to disrupt Chinese projects in the region, in light of the competition between them in different regions and issues, and especially in light of the heavy reliance of some Gulf countries on US armaments and protection from regional disturbances, not to mention the depth of US penetration of decision-making bodies in many Arab countries.
e. The broad base of religious parties and intellectual movements and the possibility of them exploiting Chinese policies towards the Uyghur minority in the western Chinese provinces (about 12 million Muslims), may constitute a relative obstacle to the Chinese initiative.
Second: The Indian Economic Corridor[8]
Map of the Economic Corridor: India – Middle East – Europe
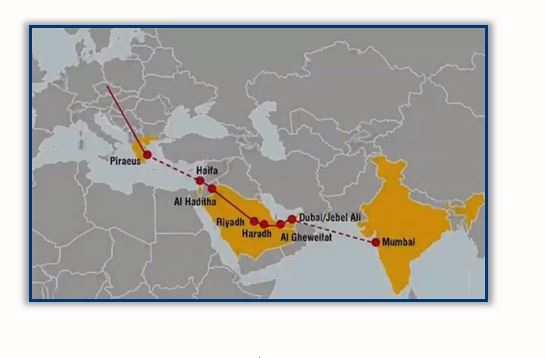
Arab-Indian relations extend back to the Sumerian period (3000 years BCE), where Persia formed a corridor for Arabs to India and China. With the advent of Islam, relations between the two sides increased, and even deepened during the colonial period and the emergence of the East India Company. Then there was the division of the Indian continent into Pakistan and India up to the contemporary period. These periods have witnessed cooperation at times and competition at others.[9]
Three factors have formed the foundations of Arab-Indian relations in the contemporary period:
1. The role of the Indian National Congress (INC) and its non-aligned policies, which brought Indian politics closer to the Arab position, under the policies of the first Indian Prime Minister after independence, Jawaharlal Nehru, regarding the Palestine issue. A stance strengthened under Prime Minister Indira Gandhi (1966–1977 and 1980–1984). India was the first non-Arab and non-Muslim country to recognize the right to self-determination of the Palestinian people, and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), granting it full diplomatic representation. Although India recognized Israel in 1950, it was until 1992 that diplomatic representation between the two sides took place, the same year China and Israel exchanged diplomatic representation.[10]
2. The increasing Indian need for Arab oil with the increasing rates of Indian development. The continued economic and technological growth in India has led to an increased need for Arab oil, especially since it is the closest energy source to the Indian continent. Until 2023, Arab oil has been covering about 60% of Indian needs, while Arab-Indian trade amounts to $240 billion, most of which with the Gulf countries, including $84 billion with UAE and $53 billion with KSA.[11]
3. The expansion of commercial and demographic relations between India and both Israel and the Arab countries, especially in the Gulf region. Until 2022, Israel was the second source of Indian arms purchases after Russia. The roots of the Indian-Israeli military cooperation extend to the periods of Indian conflict with China (1962 and 1999) and with Pakistan (1965). Israel’s share in Indian arms purchases increased from 4.7% (2010–2015) to 13% (2015–2020). The takeover of the Hindu Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) in 2014 represented a major shift in India’s weight in Israel’s military sales, as India has become the largest customer for Israeli arms, purchasing 42.1% of Israel’s military exports, followed by Azerbaijan (13.95%) then Vietnam (8.5%), all of which are Asian countries.[12]
As for the Arab world, the volume of Arab-Indian trade amounted to $240 billion, as we mentioned above, in addition to the Indian demographic presence in the region, where according to Indian government figures, there are 8.751 million Indians in the Arabian Gulf, including more than 3 million in UAE and about 2.5 million in KSA.[13] This makes Indians the second largest population group in the Arab Gulf countries after the Saudis.
All these factors formed the basis of putting forward the idea of the economic Indian-European corridor via the Middle East. Based on a memorandum of understanding between KSA, the European Union (EU), India, UAE, France, the Federal Republic of Germany, Italy and US, the participants in the G20 Summit in September 2023 committed to establish the IMEEC, to stimulate economic development, by enhancing connectivity and economic integration among Asia, the Arabian Gulf and Europe.
The corridor will consist of two separate branches: the eastern corridor connecting India to the Arabian Gulf, and the northern corridor connecting the Arabian Gulf to Europe. It will include a railway line that, when completed, will provide an efficient transit network linking existing ports to a network of railways to complement existing sea and land transport routes—allowing transit from and to India, UAE, KSA, Jordan, Israel and Europe. The participants intend to extend electricity and digital communication cables along railway routes, in addition to pipes to export clean hydrogen. This corridor will secure regional supply chains along the railway route in a way that facilitates trade flow and supports the increased focus on environmental, social and governmental impacts, all with the strategic goal of increasing efficiency, reducing costs, enhancing economic unity, generating job opportunities, and reducing emissions of greenhouse gases, thus leading to a transformative integration of Asia, Europe and the Middle East.
In support of this initiative, participants commit to working collectively and expeditiously to arrange and implement all these new transit elements. The project will connect several ports along the way, including Haifa in Israel, Piraeus in Greece and three ports on the western coast of India: Mundra, Kandla and Jawaharlal Nehru. There are five ports in the Middle East that will be linked to Indian ports, namely Fujairah, Jabal Ali and Abu Dhabi in UAE, in addition to the ports of Dammam and Ras al-Khair in KSA.
Third: India-China Competition
Most of the political units in the Arab Levant were formed during the 20th century as a result of understandings, divisions and maneuvers between European countries (since the Arab Revolt until the defeat of the Ottoman State, Sykes-Picot, the Balfour Declaration, the establishment of Israel, etc.). Thus, it is not possible to separate the geographical map or the political conditions in this region from this European, English, French, Italian and German competition.
Currently, there are two neighboring Asian countries that are rising and competing economically and technologically, namely India and China, and their rivalry has extended to the Arab region. Remarkably, the relationship between these two countries is dominated by intense competition and although China is India’s second trading partner, hostility and competition are the main characteristic of their relation, as evident in the following indicators:[14]
a. The legacy of historical hostility between the two countries which included military clashes for more than six decades, and which have been repeated, albeit with less intensity, in 1962, 1967, 1987, 2018, and 2020 and lastly in December 2022. This conflict is mainly about border areas (about 3000 kilometers), especially in the Himalayas, and about demarcating the borders between the two countries. For while China denies the occurrence of demarcation and demands it, India considers the traditional borders to be the actual borders. Another competition is taking place between the two countries in the South China Sea, especially over oil exploration in this region, in addition they have been weaving alliances against the other. This is evident in the rapprochement between China and Pakistan (India’s traditional enemy) or the Iranian-Chinese rapprochement at the expense of some decline in the Indian-Iranian relationship, not to mention the growth of the Indian-US relationship in light of the deterioration of the US-Chinese relationship, and India’s support for the blockade policies on some Chinese economic sectors.
b. with China’s presence in the region’s most important ports of Pakistan, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka, and although India has been able to relatively improve its relations with these countries.
c. India’s participation in the “Quadrilateral Security Dialogue” which was established in May 2022 and brought together the US, Japan, India and Australia, and which China considered an “Asian NATO” because it calls for deepening military relations among the four countries, in addition to economic and diplomatic cooperation.
d. The relationship between Israel and both India and China. In addition to Israel’s participation in the Chinese BRI and the Indian IMEEC, the so-called I2U2 group includes Israel, India, US and UAE, and its goal is to encourage cooperation among private sectors and businessmen in the four countries in water, energy, transportation, space, health, food security and technology, which China perceives as a kind of influence on its project, and it may also create Arab or Iranian problems with India.
Fourth: The Theory of the Spread of International Conflicts
Most studies of international relations indicate that international conflicts or wars do not remain limited to the direct parties to the conflict. Rather, tracking international conflicts and wars shows, in quantitative terms, that the vast majority of international conflicts have direct or indirect effects on neighboring and distant countries not involved in those conflicts. There is no doubt that the development of means of technical and commercial interconnection and the reduction of time and space, in light of accelerating globalization, have made preventing the repercussions of international conflicts a very complex matter. The influence and spread increase if the countries involved in the competition, conflict, or war are major countries or countries that are geographically adjacent or overlapping demographically.
Since Chinese-Indian relations are more tense, and both countries are involved in trade, geo-economic and population relations, in addition to engaging in relations with rival countries in the region (Israel and Iran, Syria and Israel, Yemen and the Gulf states, Syria and Turkey), this affects the relations of the two countries with the Arab countries on the one hand, and it may, on the other hand, add new axes to the competing axes (normalization countries and resistance countries), some of which are closer to China and others closer to India. Moreover, since the major international powers (US, Russia and some European influence) are involved in the general situation of the Middle East, the above dynamics will increase the elements of instability in the region, even though it is already the least stable region in the world.[15]
Fifth: The Future of the Region in Light of the Indian-Chinese Competition
It is necessary to determine the future of the region in light of the competition between the two Asian poles by raising a number of rhetorical questions:
1. Is the Indian project an “obstruction” to the Chinese project in light of the economic competition between the two countries, and in light of the disputes I mentioned between them? This is said while noting that Indian policy under the BJP rule has become more inclined to US policies, contrary to the Indian policy under the INC rule. Noteworthy to say about 26 Indian parties have recently allied to confront the BJP in the elections scheduled to be held early 2024. The direct support of both US President Joe Biden and Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu of the Indian project reinforces competitive concerns, especially since India is the largest customer of Israeli arms since 2014 after the BJP took control. Here, the Indian economic corridor may be a step to expand Saudi-Israeli normalization under the cover of the Indian project on the one hand, and US competition to disrupt the Chinese project on the other hand.
2. How will KSA reconcile its ties with India and with China if a severe conflict erupts between the two Asian giants?
3. Will the competition between the two projects make reaching strategic decisions in BRICS and Shanghai Cooperation Organization more complicated? Could it paralyze them, given the stark differences among the major powers in this bloc? Was the recent inclusion of “Western-oriented” countries in the BRICS a mere coincidence? or part of a plan targeting China?
4. What are the possibilities of harm to the status of the Suez Canal if the region is crossed by railway from Eilat to Haifa or directly to Haifa while bypassing the canal? Preliminary Indian studies of the project indicate that it reduces the time needed for transporting goods from Haifa to Europe, although there are discrepancies among experts in estimating this period between 4 to 6 days or between 8 to 12 days. President of the European Commission Ursula von der Leyen estimated that it would save 40% of the current time,[16] which threatens the third source of Egyptian income after remittances from workers abroad and tourism. In a study that was published in 2000 by the author, it pointed out to Israeli deliberations to make the Suez Canal less important in international transportation. It also pointed out to the encouragement of Asian projects in this field,[17] constituting a new erosion for Egypt’s economy, after the erosion inflicted by the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, which reinforces what we have suggested regarding Israeli plans to weaken Egypt in indirect ways.[18]
5. We mentioned earlier that about nine million Indian workers live in the Gulf countries (outnumbering the population of any country in the Gulf Cooperation Council except KSA), and the number of Chinese companies and employees in the Gulf countries is no less than 2.5 million people. Will this be a potential reason for the possibility of unrest between the two parties on Arab soil in case of intensification of competition and conflict between India and China?
6. Western support of the Indian project at the expense of the Chinese project: As we noted, the US, Israel, and EU have welcomed the Indian project. Indeed, media reports said that the Group of Seven (G7) countries pledged at their meeting in Tokyo in May 2023 to collectively mobilize $600 billion by 2027 to to counter the BRI, noting that the Chinese project has been supported by 150 countries and 30 international organizations, mobilizing nearly $1 trillion and creating over 3 thousand projects. The project is targeted for completion by 2049.[19] Will this polarization between the two projects be employed to manage their conflict on Arab soil?
7. Will the Arab countries, especially the Gulf countries (such as KSA and UAE), or those through which either or both projects (the Indian and the Chinese) pass, find themselves faced with the need to choose between the two giants, as Italy did when it announced that it would withdraw from the Chinese project? What about the positions of the nine million Indians if an Arab country takes a position opposed to the Indian position?
8. What are the possibilities and indicators of militarization of the two projects? India has conducted military exercises with some countries in the region, such as KSA, UAE, the Sultanate of Oman and Egypt in 2023,[20] and each time the scope of the exercises between the two sides expands. Since 2019, the Indian Navy has been conducting Operation Sankalp, under which its warships have been tasked with providing security for Indian-flagged vessels, specifically oil tankers, as they navigate the Strait of Hormuz and Gulf of Oman amid heightened tensions between Iran, US and others in the region. The Indian Navy has stationed a liaison officer at US Central Command (CENTCOM) in Bahrain, with the same personnel tasked with developing India’s cooperation with the Manama-based Combined Maritime Forces, a 38-nation maritime partnership that also includes Pakistan (India’s traditional adversary). These developments were cemented during the April 2020 2+2 ministerial dialogue between New Delhi and Washington. This clearly indicates two dimensions in Indian planning in the region: the strategic dimension and the economic dimension, which requires asking a central question: How will India reconcile its strategy toward Israel, Iran and KSA with all the differences among these important regional parties? China, for now, has managed to do this by leveraging its economic heft and regional states’ interest in using Beijing as a counterbalance to the US. “India will need to find other ways to strike a balance, specifically in its relations with Iran, which face the sanctions regime Washington has put in place.” Indeed, “New Delhi halted energy imports from Tehran both to comply with sanctions and in a show of intent to the US. This decision has come into question, especially after India picked up cheap Russian crude oil despite sanctions amid the war in Ukraine.”[21]
9. What if the two countries (China and India) begin to militarize their presence at a later stage, as we mentioned in the indicators and possibilities of militarization in the previous point? If the dispute and competition between them escalates, will India China establish bases in the Gulf states, Pakistan, or in the countries of the Horn of Africa from Djibouti to Sudan to protect their interests? This will increase the indicator of militarization in the Middle East. In addition to the Indian policies we mentioned in the course of militarization, China has carried out military activities to protect its citizens in a number of Arab countries or to rescue them during periods of instability, and it established some military bases or facilities for them, which was made clear in the White Paper released in 2019 by China’s State Council Information Office which stipulated the protection of Chinese interests, individuals and bodies abroad. This is not to mention arms sales to countries along the Road and Belt, where for example, 47% of Chinese arms sales during the 2017–2021 period were directed to Pakistan (India’s traditional enemy), while from 2012 to 2021, China’s military exports grew by 290% to KSA and by 77% to the UAE.[22]
Conclusion
The previous data indicate:
1. The importance of the Arab region to both China and India (as markets, energy sources and large labor absorption sites) makes the two Asian giants more eager to be present in the region.
2. The Chinese-Indian disputes are deep and may push the Arab region to forge political, economic or military connections, in order to manage the Chinese-Indian conflict there, especially in light of the lack of a unified Arab strategy.
3. The Gulf region may experience social unrest if Arab countries adopt policies inconsistent with the orientations of the two Asian countries, and it seems that this possibility is higher with India than with China.
4. If the interests of the two countries expand, the possibilities of militarization of the region are not excluded, which will impact the region’s policies and stability, especially if the Asian competition is accompanied by Western alliances with India, particularly by the US in the Middle East, all in order to confront the Chinese project.
5. Israel is trying to maintain its relations with the two Asian powers, and it appears to be reasonably successful in this aspect, which constitutes a challenge to some regional powers such as Iran, Syria and other Arab resistance wings. This requires the Arab side to support communication with the Indian opposition to the BJP, especially the INC, and to maintain “communication” with the less pragmatic trend in the Chinese Communist Party to benefit from its recommendations towards the region.
6. The strategic prospects of the Indian and Chinese projects indicate two conflicting possibilities:
a. Transforming the conflict in the region from a zero-sum conflict into a non-zero-sum conflict by integrating Israel into the heart of Arab-Asian projects, which is what Israel as well as India and China seek. This will expand the circle of common interests among the parties to the projects at the expense of the contradictory interests at the heart of which is the Palestine issue.
b. The failure of the first possibility means an increase in Asian competition between the Indian and Chinese projects, which may lead to the militarization of the region and an increase in regional polarization of the two projects. This will drag the region into new conflicts and higher levels of instability, especially since the Western side will remain present in these polarizations during the coming medium period, thus making the situation more complicated.
[1] An expert in futures studies, a former professor in the Department of Political Science at Yarmouk University in Jordan and a holder of Ph.D. in Political Science from Cairo University. He is also a former member of the Board of Trustees of Al-Zaytoonah University of Jordan, Irbid National University, the National Center for Human Rights, the Board of Grievances and the Supreme Council of Media. He has authored 37 books, most of which are focused on future studies in both theoretical and practical terms, and published 120 research papers in peer-reviewed academic journals.
[2] The geopolitical concept is centered on the mutual influence between geographic variables and internal and external political behavior while the geostrategic concept is centered on planning based on identifying different geographical areas or regions that are more strategically important in their geographical location to achieve the state’s goals. For example, a country like Afghanistan cannot build a naval fleet since it is landlocked, but the first thing that Britain or Japan might think about is building a fleet. The geostrategic concept plans how to employ the strategic position of the geography to formulate the country’s foreign policy. For example, the strategic value of the location of Afghanistan cannot be compared to the location of Nepal from the perspective of the major and central countries competing on the international stage. The Egyptian writer Gamal Hamdan’s expression “the genius of place” can be considered a geostrategic expression, especially when he refers to the location or place, Egypt’s strategic character, and the heart of the world. See: Gamal Hamdan, Shakhsiyyat Masr: Dirasah fi ‘Abqariyyat al-Makan (Egypt’s Personality: A Study in the Genius of Place) (Dar al-Hilal, 1967), Chapter 25 entitled Egypt’s Strategic Personality and Chapter 26 entitled The Heart of the World.
While Ali al-Wardi’s expression of the influence of the desert and the sea on Iraqi social behavior, including his political behavior, is an expression of the reflection of the natural geographical nature on political behavior, which represents geopolitics. See details in: Ali al-Wardi, Shakhsiyyat al-Fard al-‘Iraqi: Bahth fi Nafsiyyat al-Sha‘b al-‘Iraqi ‘ala Daw’ ‘Ilm al-Ijtima‘ al-Hadith (The Personality of the Iraqi Individual: An Investigation into the Psychology of the Iraqi People in Light of Modern Sociology), 2nd edition (London: Dar Laila Publications, 2001), pp. 48-55, and 75-78. See also Jan Wendt, “The Select Methods of Investigations in Geostrategy and Geopolitics,” Political Geography Studies in Central and Eastern Europe, Oradea, 2000, https://depot.ceon.pl/bitstream/handle/123456789/5344/The_select_methods_of_investigations_in_geostrategy_and_geopolitics.pdf?sequence=1
[3] Walid ‘Abd al-Hay, Dirasat Mustaqbaliyyah fi al-‘Alaqat al-Duwaliyyah: Namadhij Tatbiqiyyah (Futures Studies in International Relations: Applied Models) (Beirut: Al-Zaytouna Centre for Studies and Consultations, 2023), pp. 82-83.
[4] Fazzur Rahman Saddiqui, China and The Arab World: Past and Present (New Delhi: Indian Council of World Affairs, Sapru House Paper, 2022), pp. 84-92.
[5] Walid Abd al-Hay, Does the Balancing Policy Restrict China’s Role in the Middle East? International Politics Journal, Al-Ahram Foundation, Issue 207, January 2017, p. 26. (in Arabic)
[6] Ruby Osman, Bye Bye BRI? Why 3 New Initiatives Will Shape the Next 10 Years of China’s Global Outreach, site of Time, 1/10/2023, https://time.com/6319264/china-belt-and-road-ten-years
[7] Christoph Nedopil Wang, “Brief: China Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) Investment Report 2021,” site of Green Finance & Development Center, 2/2/2022, https://greenfdc.org/brief-china-belt-and-road-initiative-bri-investment-report-2021; and NC Bipindra, China Completes 10 Years Of $1.4 Trillion BRI Project; Puts South Asia, Barring India & Bhutan, In A Bind, site of The EurAsian Times, 23/7/2023, https://www.eurasiantimes.com/china-completes-10-years-of-1-4-trillion-bri-project-puts
[8] Memorandum of Understanding on the Principles of an India – Middle East – Europe Economic Corridor, site of The White House, 2023, https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Project-Gateway-Multilateral-MOU.pdf; and Rajeswari Pillai Rajagopalan, The Geopolitics of the New India-Middle East-Europe Corridor, site of ORF, 29/9/2023, https://www.orfonline.org/research/the-geopolitics-of-the-new-india-middle-east-europe-corridor
[9] For further details, see Hojjatollah Hezariyana and Ghaffar Pourbakhtiarb, A Historical Study of the Persian Gulf and Indo-Arab Trade Until the 5th Century AH, Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education, vol. 12, No. 11, 2021, pp. 6724-6725.
[10] Sujata Ashwarya, “India’s policy towards the Arab–Israeli conflict, the Palestinian issue and Israel: the Indira Gandhi years,” Global Discourse journal, Bristol University Press, vol. 13, No. 23, 2022, pp. 2-5.
[11] New Trade Initiative Offers India Major Gains in Middle East, site of VOA News, 27/9/2023, https://www.voanews.com/a/new-trade-initiative-offers-india-major-gains-in-middle-east/7287689.html
[12] Azad Essa, India and Israel: The arms trade in charts and numbers, site of Middle East Eye, 31/5/2022, https://www.middleeasteye.net/news/india-israel-arms-trade-numbers
[13] Question No. 583 Indian Workers in Gulf Countries, site of Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India, 9/12/2022, https://www.mea.gov.in/lok-sabha.htm?dtl/35979
[14] Derek Grossman, India Is Pushing Back Against China in South Asia, site of The Rand Blog, 21/8/2023, https://www.rand.org/blog/2023/08/india-is-pushing-back-against-china-in-south-asia.html; I2U2: India, Israel, United Arab Emirates, United States, site of U.S. Department of State, https://www.state.gov/i2u2; Vijay Gokhale, Shivshankar Menon, and Tanvi Madan, A big-picture look at the India-China relationship, site of Brookings Institution, 20/9/2023, https://www.brookings.edu/articles/a-big-picture-look-at-the-india-china-relationship; What Kind of Group Is the 4-nation Quad?, site of Learning English, VOA news, 24/5/2022, https://learningenglish.voanews.com/a/what-kind-of-group-is-the-4-nation-quad-/6587184.html; YP Rajesh, Krishn Kaushik and Martin Quin Pollard, Xi skipping G20 summit seen as new setback to India-China ties, site of Reuters, 5/9/2023, https://www.reuters.com/world/xi-skipping-g20-summit-seen-new-setback-india-china-ties-2023-09-05; and Aleksandra Gadzala Tirziu, Rising tensions along the Indian-Chinese border, site of Geopolitical Intelligence Services, 8/8/2023, https://www.gisreportsonline.com/r/china-india-border-2
[15] Hasan Alhasan, The China-India Contest in the Middle East, site of The Diplomat, 21/7/2020, https://thediplomat.com/2020/07/the-china-india-contest-in-the-middle-east
[16] India-Middle East-Europe economic corridor to counter China?, site of Deutsche Welle (DW), 13/9/2023, https://www.dw.com/en/can-new-india-europe-middle-east-corridor-counter-china/a-66799232
[17] Walid Abd al-Hay, “The Future of the Strategic Position of the Arab World,” Journal of Strategic Issues, Arab Center for Strategic Studies, Issue 4, December 2000, pp. 146-147. (in Arabic)
[18] Walid ‘Abd al-Hay, The Future of Egyptian-Israeli Relations from the Israeli Perspective, site of al-Zaytouna Centre for Studies and Consultations, 5/6/2023, https://www.alzaytouna.net
[19] India-Middle East-Europe economic corridor to counter China?, DW, 13/9/2023.
[20] Indian Army to participate in largest ever joint military exercise in Middle East, says MoD, site of The Economic Times, 29/8/2023, https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/defence/indian-army-to-participate-in-largest-ever-joint-military-exercise-in-middle-east-says-mod/articleshow/103176080.cms?from=mdr; and India, UAE conclude joint Arabian Gulf naval exercise, site of Arab News, 12/8/2023, https://www.arabnews.com/node/2354021/world
[21] Kabir Taneja, How India views China’s diplomacy in the Middle East, site of Middle East Institute, 11/7/2023, https://www.mei.edu/publications/how-india-views-chinas-diplomacy-middle-east
[22] For details on China’s militarization activities, see Guo Yuandan and Liu Xuanzun, PLA Navy’s 14 years of missions in blue waters safeguard intl trade routes, win more overseas recognition, site of Global Times, 1/8/2022, https://www.globaltimes.cn/page/202208/1271933.shtml
China increasing arms exports to Middle East and Eastern Europe, site of The Nation, 5/12/2022, https://www.nationthailand.com/world/china/40022762; Chinese Private Security Companies Along the BRI: An Emerging Threat?, site of Modern Diplomacy, 25/9/2020, https://moderndiplomacy.eu/2020/09/25/chinese-private-security-companies-along-the-bri-an- emerging-threat; Chinese army prioritizes protecting China’s overseas interests, site of China Global Television Network (CGTN), 24/7/2019, https://news.cgtn.com/news/2019-07-24/Chinese-army-prioritizes-protecting-China-s-overseas-interests-IA9FouJ5ZK/index.html; and Andrea Ghiselli, Continuity and change in China’s strategy to protect overseas interests, site of The Frontier Post, 2021, https://thefrontierpost.com/continuity-and-change-in-chinas-strategy-to-protect-overseas-interests
| Click here to download: >>Academic Paper: The Arab Levant: From Western to Asian Competition … Prof. Dr. Walid ‘Abd al-Hay |




Leave A Comment